The United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) began publishing recommendations on cancer drugs in 2000. Nearly three-quarters of these recommendations are positive: either recommended, optimized or recommended for use in the Cancer Drugs Fund (CDF).
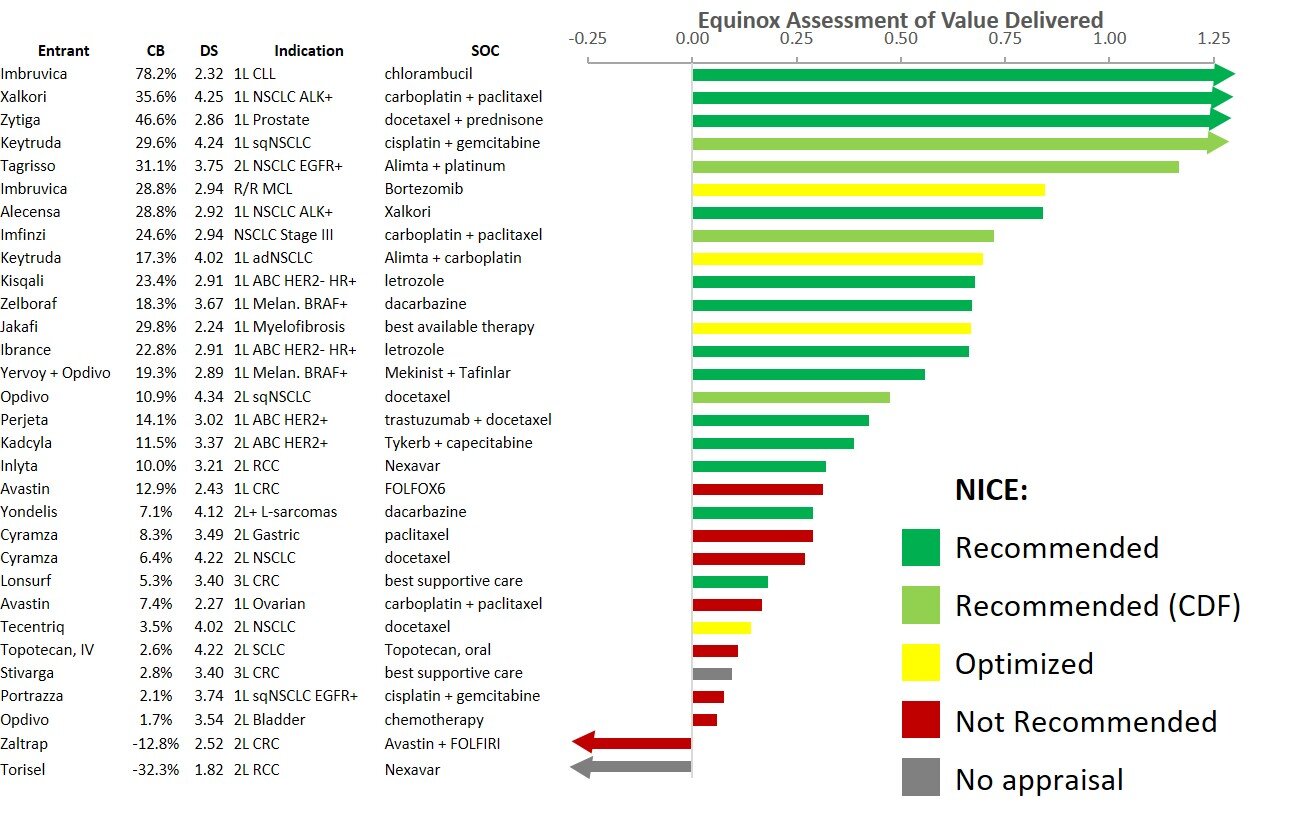
We looked at the 31 instances of drugs/indications that Equinox had assessed and that received or could have received NICE appraisals (in two instances, companies declined to seek appraisal). As the table below shows, we find a strong correspondence between Equinox’s evaluation of innovation for an agent in an indication and the result of the NICE appraisal, whether positive (recommended, optimized or recommended for use in the CDF) or negative (not recommended or no appraisal).
Note: “Innovative” means 5% or higher on Equinox Group’s Clinical Innovation metric
As with NICE’s evaluation of cost-effectiveness, Equinox employs a robust method to calculate the magnitude of value delivered, which depends on the clinical benefit a drug offers as well as the seriousness of the disease that it treats. In the figure below, the value delivered for the same 31 instances of drug/indications is color-coded based on NICE recommendation status.
Overall, we see that Equinox’s measures of clinical innovation and of value delivered are compelling predictors of the recommendations NICE will ultimately make.